Kirchhoff’s Laws Explained Simply: The Backbone of Every Electrical Circuit
Kirchhoff’s Laws are the foundation of electrical circuit analysis. These two powerful laws—Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) and Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL)—explain how current and voltage behave in complex circuits. This article breaks down Kirchhoff’s Laws in a simple, visual, and beginner-friendly way, making them easy to understand for students, engineers, and electronics enthusiasts.Learn Kirchhoff’s Laws with simple explanations and diagrams. Understand KCL and KVL to analyze any electrical circuit easily and accurately.

Kirchhoff’s Law – Explanation with Examples and Diagram
Kirchhoff’s Law is one of the most important concepts in electrical and electronics engineering. It is used to analyze simple as well as complex electrical circuits where Ohm’s Law alone is not sufficient.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to Kirchhoff’s Law
2. Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL)
3. Example of KCL
4. Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL)
5. Example of KVL
6. Circuit Diagram
7. Applications of Kirchhoff’s Law
8. Conclusion
1. Introduction to Kirchhoff’s Law
Kirchhoff’s Law consists of two basic laws introduced by German scientist Gustav Robert Kirchhoff in 1845.
These laws are based on the principles of conservation of charge and conservation of energy.
Kirchhoff’s Laws are widely used for analyzing DC and AC circuits, especially complex networks with multiple loops and nodes.
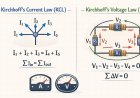
2. Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL)
Kirchhoff’s Current Law states that:
The total current entering a node is equal to the total current leaving that node.
In simple words, current cannot disappear or be created at a junction.
Mathematical form:
Sum of incoming currents = Sum of outgoing currents
This law is based on the conservation of electric charge.
3. Example of Kirchhoff’s Current Law
Consider a node where two currents enter and one current leaves.
I₁ = 3 A (entering the node) I₂ = 5 A (entering the node)
According to KCL:
I₃ = I₁ + I₂ I₃ = 3 A + 5 A = 8 A
Thus, the current leaving the node must be 8 A.
4. Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL)
Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law states that:
The algebraic sum of all voltages around any closed loop in a circuit is zero.
This means that the total energy supplied by the sources is equal to the total energy consumed by the circuit elements.
Mathematical form:
ΣV = 0
5. Example of Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law
Consider a simple loop containing one battery and two resistors.
Battery voltage = 12 V Voltage drop across R₁ = 4 V Voltage drop across R₂ = 8 V
Applying KVL:
12 V − 4 V − 8 V = 0
This verifies Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law.
6. Simple Circuit Diagram

Sign Conventions:

7. Applications of Kirchhoff’s Law
Kirchhoff’s Laws are used in:
DC and AC circuit analysis Network theory Electrical and electronics engineering Power systems and control systems Design and analysis of electronic devices
8. Conclusion
Kirchhoff’s Law is a fundamental tool for understanding and analyzing electrical circuits.
By applying KCL and KVL, even very complex circuits can be solved in a systematic and logical way.
Therefore, Kirchhoff’s Laws are essential for every student and professional in the field of electrical engineering.
Electrical First Year के सभी Question Papers डाउनलोड करने के लिए नीचे दिए गए लिंक पर क्लिक करें।




































.svg)