AC Terminology & Sinusoidal Waveforms Made Easy for AKTU Students | Complete Exam Guide
Learn AC Terminology and Representation of Sinusoidal Waveforms in the easiest way for AKTU Electrical Engineering exams. Includes RMS value, frequency, phase angle, waveform diagram, formulas, and important FAQs for university exams.

AC Terminology & Representation of Sinusoidal Waveforms
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to Alternating Current
2. Basic AC Terminology
3. Cycle and Time Period
4. Frequency of AC Signal
5. Angular Frequency
6. Phase and Phase Difference
7. Instantaneous Value
8. Peak Value
9. RMS Value
10. Average Value
11. Form Factor
12. Crest Factor
13. Sinusoidal Waveform
14. Mathematical Representation
15. Phasor Representation
16. Graphical Representation
17. Importance in Electrical Engineering
18. Conclusion
1. Introduction to Alternating Current
Alternating Current is one of the most important concepts in electrical engineering, especially for AKTU first year students who are studying Basic Electrical Engineering. Unlike direct current, alternating current continuously changes its magnitude and direction with respect to time. In real life applications, most of the electrical power that we use in our homes, industries, and commercial systems is supplied in the form of AC.
Alternating current follows a periodic waveform which repeats itself after a certain time interval. The most common waveform used in AC systems is the sinusoidal waveform because it is easy to generate and transmit over long distances with minimum loss. Understanding AC terminology and sinusoidal waveform representation is essential for analyzing electrical circuits and machines.

2. Basic AC Terminology
Before understanding sinusoidal waveforms, students must learn the basic AC terminology used in electrical engineering. Some of the important AC terms include cycle, time period, frequency, amplitude, phase angle, RMS value, average value, and instantaneous value.
These terms help engineers understand the behavior of alternating signals and analyze the performance of electrical circuits effectively.

3. Cycle and Time Period
A cycle is defined as one complete set of positive and negative values of an alternating quantity. When an AC waveform starts from zero, reaches its positive maximum value, comes back to zero, reaches its negative maximum value, and again returns to zero, it is said to complete one cycle.
The time taken by an AC waveform to complete one full cycle is known as the time period. It is denoted by the symbol T and is measured in seconds.
4. Frequency of AC Signal
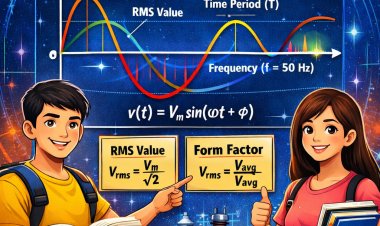
Frequency is defined as the number of cycles completed by an AC waveform in one second. It is represented by the symbol f and is measured in Hertz. In India, the standard frequency of AC supply is 50 Hz.
Mathematically, frequency is the reciprocal of time period:
f = 1/T
5. Angular Frequency
Angular frequency represents the rate of change of phase angle with respect to time. It is denoted by omega (ω) and is measured in radians per second.
ω = 2πf
6. Phase and Phase Difference
Phase indicates the position of a waveform with respect to a reference waveform. When two waveforms reach their maximum and minimum values at the same time, they are said to be in phase.
If two waveforms reach their corresponding values at different times, they are said to be out of phase. The difference between the phases of two waveforms is known as phase difference.

7. Instantaneous Value
The value of alternating voltage or current at any instant of time is known as the instantaneous value. It keeps on changing with time according to the waveform.
8. Peak Value
Peak value is the maximum value attained by an AC quantity in either positive or negative direction. It is also known as the maximum value or amplitude.
9. RMS Value
The RMS value of an alternating quantity is defined as the square root of the mean of the squares of all instantaneous values over one complete cycle.
For a sinusoidal waveform:
Vrms = Vm / √2
10. Average Value
The average value of an AC quantity is the arithmetic mean of all instantaneous values over one half cycle.
Vavg = 0.637 Vm
11. Form Factor
Form factor is defined as the ratio of RMS value to average value.
Form Factor = Vrms / Vavg
12. Crest Factor
Crest factor is defined as the ratio of peak value to RMS value.
Crest Factor = Vm / Vrms

13. Sinusoidal Waveform
A sinusoidal waveform is the most common type of AC waveform used in electrical systems. It follows a sine curve and is represented mathematically by trigonometric functions.
14. Mathematical Representation
The general equation of a sinusoidal alternating voltage is:
v(t) = Vm sin(ωt + φ)
Where Vm is the maximum value, ω is angular frequency and φ is phase angle.
15. Phasor Representation
Phasor representation is a graphical method used to represent sinusoidal quantities in terms of magnitude and phase angle using rotating vectors.
16. Graphical Representation
In graphical representation, sinusoidal waveforms are plotted with time on the horizontal axis and voltage or current on the vertical axis.
17. Importance in Electrical Engineering
Understanding AC terminology and sinusoidal waveform representation helps students analyze AC circuits, transformers, motors, and power systems efficiently.
18. Conclusion
AC terminology and sinusoidal waveform representation form the foundation of electrical engineering studies for AKTU students. A clear understanding of these concepts is necessary for analyzing electrical circuits and machines in future semesters.
Click Here to Download Complete Syllabus of First Year
Previous Year Question Paper Of FEE(Click Here to Download)
Previous Year Question Papers Of All Subjects Related with First Year(Click Here)


































.svg)